
Integrated Cloud Communication Security in Today’s Cloud Workspace
Integrated Cloud Communication Security in Today’s Cloud Workspace
Using Context Analysis to Detect Language-Based Attacks

Download: Understand the risks to your enterprise business communications in today's cloud workspace.

Executive Summary
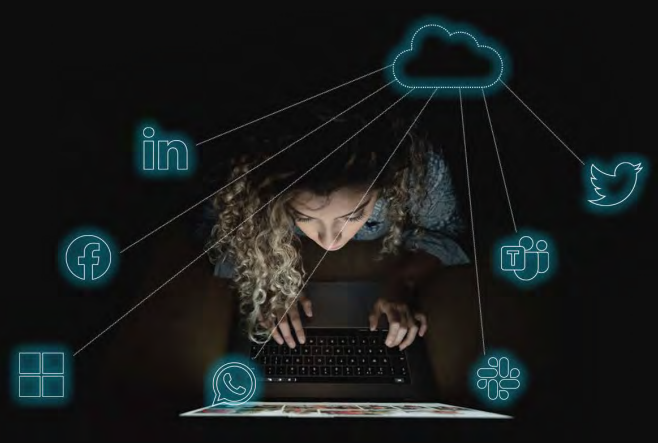
Humans are the most vulnerable part of any organization's cybersecurity defenses. The growing remote workforce and expanding use of digital communication channels is helping bad actors renew their efforts to steal data and extort funds with adapted tactics. With 45% of business communications occurring outside of email in channels such as Teams or Slack, to personal apps like LinkedIn, attackers are increasingly using social engineering and other language based attacks to skirt around existing email security solutions.
Attacks come in many shapes and forms, from ransomware and account takeover, to fraud, business email compromise (BEC), ransomware, and more. To counter these threats, organizations need to retool their security systems to gain full visibility across all workspace channels and enable the use of NLU-based (Natural Language Understanding) Context Analysis to understand the context and intent of business communications.
45%
of U.S. companies experienced a data breach in 2021
82%
of data breaches involved the human element in 2021
Evolving Threat Landscape
In general, humans are the weakest link in an organizations’ cybersecurity defenses. In 2022, 25% of all breaches were the result of social engineering attacks. When including human error and misuse of privilege, that number jumps to 82% of breaches linked to humans over the past year. According to a recent article in SC Magazine, language-based attacks are now the new normal for business email compromises (BECs) with nearly 75% of attacks using language as the main attack vector. In addition to language, malicious links, weaponized payloads, and common business workflows have become a common proxy to compromise employees and steal money, credentials, or sensitive data. Here are just a few ways bad actors are targeting human nature.

Social Engineering Threats
Bad actors use social engineering to trick individuals into sharing sensitive information. Actors use social engineering to exploit basic human nature and often revolve around fear, greed, curiosity, helpfulness, and urgency. Common social engineering attacks include phishing, spear phishing, business email compromise, and impersonation. “According to cloud security company Zscaler, 2021 saw a 29% rise in phishing attacks, driven – it believes, in part – by phishing as a service (PhaaS). Across retail and wholesale, a 400% increase in phishing attacks was observed over the last 12 months, while financial and governmental sectors saw a more-than 100% increase. PhaaS puts pre-built attack tools up for sale in underground marketplaces online, making it easier for non-sophisticated actors to launch successful attacks.”

Insider Threats
Insider threats are typically delivered by three types of actors: careless users, malicious insiders, and credential thieves. Careless users inadvertently expose sensitive data by making simple errors or by misconfiguring their defenses. In one common example, healthcare workers email protected healthcare information to the wrong email recipient – a result of address autofill. Malicious insiders intentionally sabotage their employer or steal information for either personal reasons or financial gain. Credential thieves slip through security controls using stolen credentials and go about stealing data or conducting sabotage. While insider threats can be less of a problem than by the activities of external actors, these types of incidents have risen 44% over the past two years, with costs per incident up more than a third to $15.38 million.
Malware and Ransomware Threats
Ransomware attacks put critical data at risk of theft or destruction while rendering IT systems inoperable. These attacks are sophisticated forms of malware that are costly to virtually every enterprise, regardless of size or vertical focus. On average, organizations are effectively disabled for 19 days, on average. Ransomware caused at least $8.0 billion in damages in 2018, growing to $11.5 billion in 2019. During 2021, approximately 37% of global organizations were victims of some form of ransomware attack, resulting in $20 billion in damages.

Multi-Channel Threats
As mentioned above, email-based phishing and spear phishing are favorite vectors of attacks and SecOps teams have put in place email security solutions to thwart them. Attackers are adapting their tactics to target users via unprotected social media accounts, mobile chat, and digital collaboration applications. Social media apps like Facebook, collaboration apps such as Microsoft Teams, Slack, and Zoom, and messaging apps like WeChat and Telegram have quickly become embedded in today’s brands and business relationships. These apps allow employees and executives to enter places beyond the usual scope of enterprise data management.
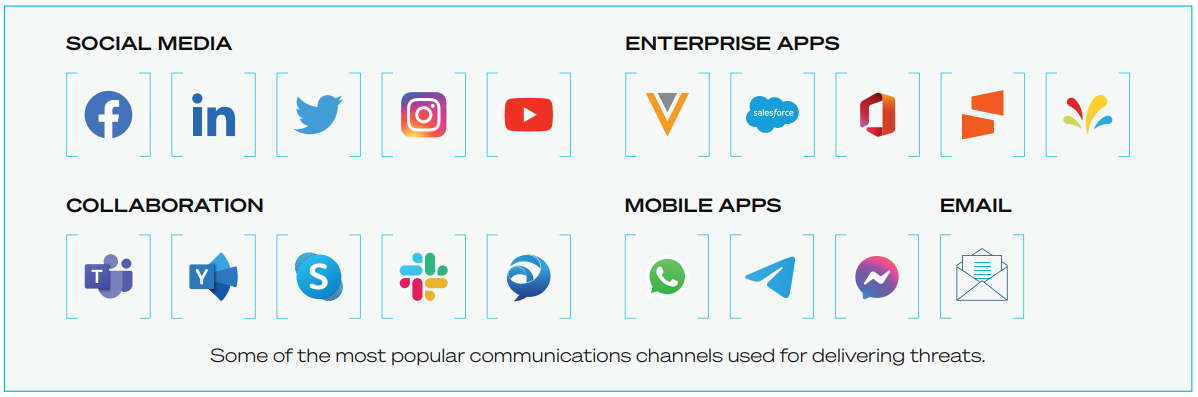 Some of the most popular communications channels used for delivering threats.
Some of the most popular communications channels used for delivering threats.
Attackers, especially those attempting to commit fraud, impersonation, and business compromise, are evading detection by starting communications in email and then quickly moving conversations to unprotected channels such as Slack or Teams. For this reason, focusing on email is not enough for a comprehensive defense strategy. Security practitioners must provide universal security coverage that determines user identity, behavior analytics, content, and context across all supported communication channels.
Retooling Security with Contextual Analytics
To identify ‘good’ conversations from those representing threats, NLU-based contextual analytics help SOC teams determine the context and intent of communications. Sophisticated ML models use NLU derived context and intent with message metadata to accurately identify threats. This helps security teams take action earlier in the kill chain, before a harmful payload is delivered or credentials are compromised. This approach serves as an added layer of detection that complements existing email security, giving organizations a more proactive threat detection and response capability that can prevent theft and loss before they occur.

Detected threats include email compromise, fraud
(invoice, payment, payroll), insider threat, credential theft, impersonation, and account takeover.
SafeGuard Cyber NLU Platform
The SafeGuard Cyber platform is a third generation solution that uses NLU and ML to understand the context and intent of human digital communications. It is designed with the SOC in mind, using API integration with communication channels and security infrastructure to make the platform easy to deploy, simple to use, and quick to operationalize.
This patented detection engine accurately identifies social engineering attacks by analyzing a comprehensive set of message features, including:
- Digital Identity - verifying the sender’s identity
- Semantic Analysis - understanding the content of the message
- Metadata Traits - analyzing characteristics of the message
- Behavior Analytics - identifying abnormal behavior
- Social Graph Analysis - analyzing the history of past communication
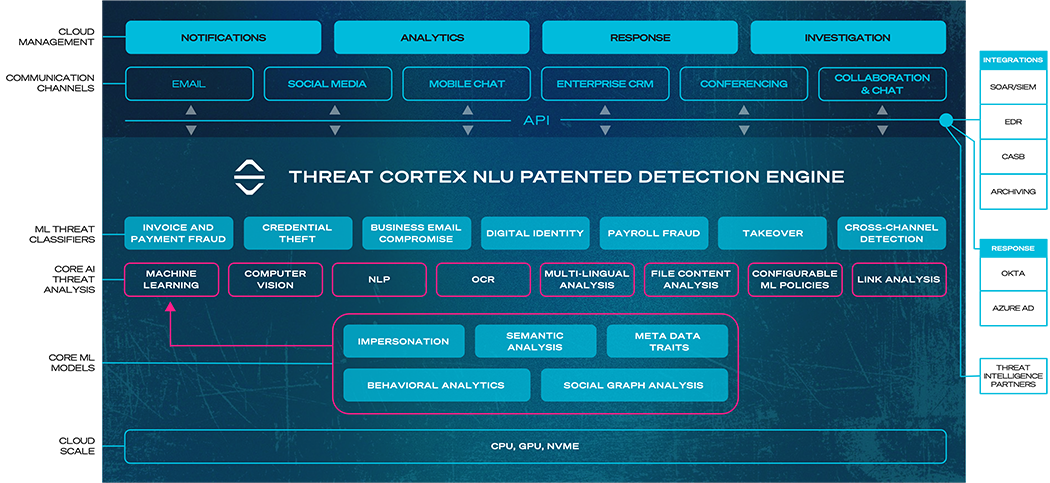
Threat Detection Analytics and Responses
Through a single pane of glass interface, the SafeGuard Cyber platform provides real-time detection and analysis of events within and across workspace channels. Unlike pure behavioral detection solutions, the SafeGuard Cyber platform uses multilingual NLU technology to identify the context and determine intent of communications. While ICES solutions focus on email, SafeGuard Cyber expands the security umbrella to protect 30 other business channels for collaboration, chat, conferencing, social media, and mobile messaging. And unlike CASB solutions that only focus on cloud data protection, SafeGuard Cyber collectively monitors cross-channel activity to detect sophisticated attack campaigns that span multiple channels.
